BMI Calculator
Enter weight and height to calculate BMI
Fill in data to calculate your healthy weight rangeDisclaimer: This BMI calculator is for informational and educational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Please consult a qualified healthcare provider for personalized health guidance.
What Is BMI?
Body Mass Index (BMI) is a simple and widely recognized tool used to evaluate whether a person’s weight is healthy in relation to their height. It helps doctors and healthcare professionals estimate body fat and assess the risk of conditions like heart disease, diabetes, and high blood pressure.
Fun fact: BMI was originally called the Quetelet Index, named after the Belgian mathematician Adolphe Quetelet who developed it in the 19th century. It wasn’t until 1972 that physiologist Ancel Keys reintroduced it as the 'Body Mass Index' and highlighted its usefulness in public health research and medical assessments.
The BMI calculator on this page is designed for adults between the ages of 18 and 65 and can be used worldwide.
Keep in mind that BMI categories may vary depending on factors like age (for children or seniors), ethnicity, pregnancy, physical disabilities, or higher-than-average muscle mass.
For a more accurate assessment of your health, BMI should be used alongside other key measurements like waist-hip ratio, waist circumference, visceral fat levels, and the Body Adiposity Index (BAI).
How is BMI Calculated?
Calculating your Body Mass Index (BMI) is simple. You just divide your weight by the square of your height.
-
If you're using metric units:
BMI = weight (kg) ÷ [height (m)]²
-
If you're using imperial units::
BMI = weight (lb) ÷ [height (in)]² × 703
This quick formula helps estimate which BMI range your weight falls based on your height, as defined by World Health Organization (WHO).
Different BMI Categories and What They Mean?
Below are the WHO defined global BMI categories and there meanings.
Underweight (BMI below 18.5): Being underweight may signal malnutrition or an underlying health issue that should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Healthy Weight (BMI 18.5 - 24.9): This range is generally considered healthy for most adults and is associated with a lower risk of weight-related health conditions.
Overweight (BMI 25 - 29.9): Individuals in this range may face a higher risk of health problems such as heart disease, high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes.
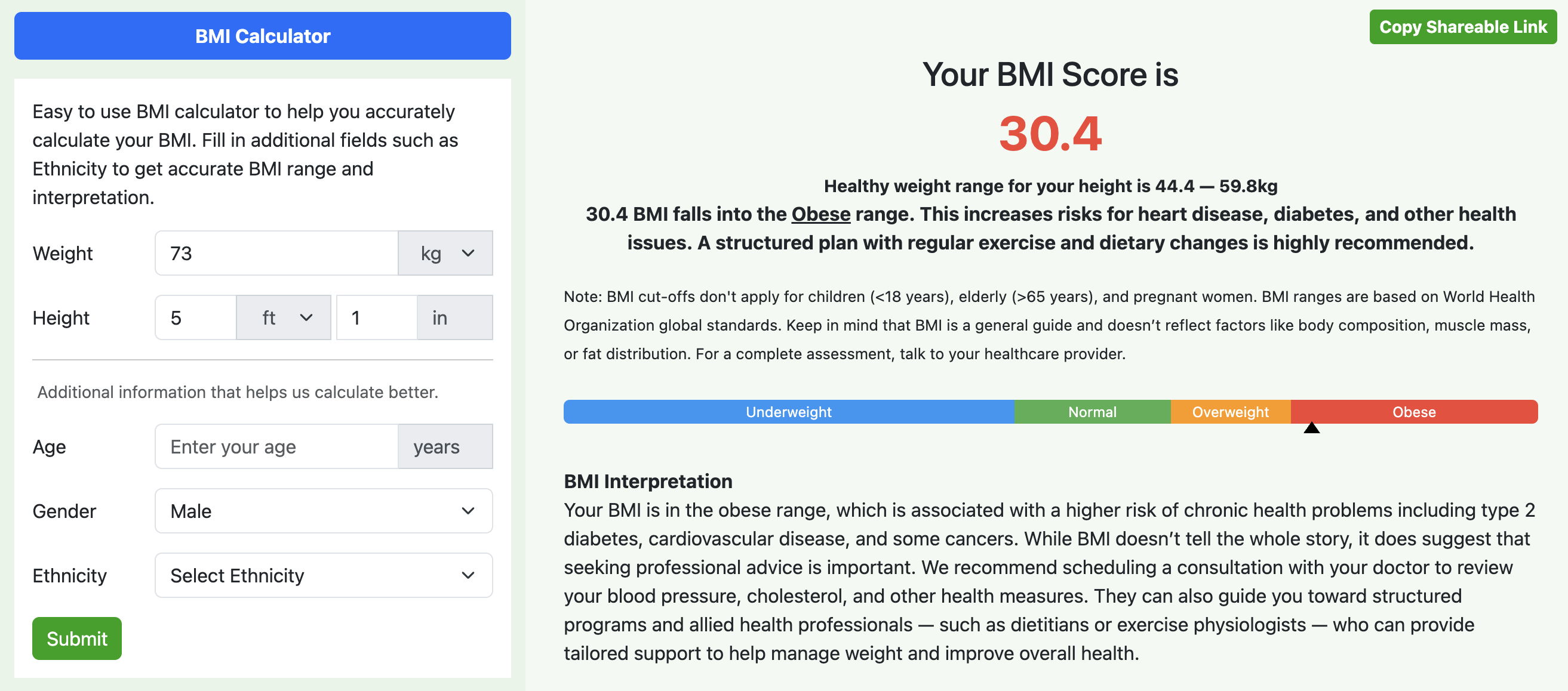
Obese (BMI 30 and above): Obesity is typically divided into three classes (Class I, II, and III). A BMI of 30 or higher increases the risk of serious health issues and may require medical guidance, lifestyle changes, or weight management strategies.
BMI Chart for Adults (Between 18 and 65 years)
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), the following BMI classifications apply to both men and women aged 18 and above:
| Category | BMI Range |
|---|---|
| Severe Thinness | Less than 16 |
| Moderate Thinness | 16 - 16.9 |
| Mild Thinness | 17 - 18.4 |
| Normal Range (Healthy Weight) | 18.5 - 24.9 |
| Overweight | 25 - 29.9 |
| Obesity Class I | 30 - 34.9 |
| Obesity Class II | 35 - 39.9 |
| Obesity Class III | 40 and above |
BMI Chart for Children and Teens (Ages 2 to 18)
For children and adolescents, BMI is interpreted using percentiles, as recommended by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
| Category | BMI Percentile Range |
|---|---|
| Underweight | < 5th percentile |
| Healthy Weight | 5th percentile - < 85th percentile |
| Overweight | 85th percentile - < 95th percentile |
| Obese | > 95th percentile |
If your BMI falls outside the healthy range, it’s a good idea to consult a healthcare provider. They can offer a more personalized assessment based on your age, lifestyle, body composition, and overall health.
BMI cut-off values may differ by ethnicity. For example, Asian populations may face higher health risks at lower BMI levels. Health authorities recommend the following adjusted BMI categories for Asian adults:
BMI Chart for Asian Adults (Between 18 and 65 years)
| Category | BMI Range |
|---|---|
| Underweight | Less than 18.5 |
| Healthy Weight | 18.5 - 22.9 |
| Overweight | 23.0 - 24.9 |
| Obese | 25 and above |
Example: How to Calculate BMI?
Let’s walk through a simple BMI calculation using both metric and imperial units.
Using Metric Units: If someone weighs 70 kilograms and is 1.75 meters tall:
BMI = 70 / (1.75 ^ 2) = 70 / 3.06 = 22.9 (approx.)
A BMI of 22.9 falls within the "normal weight" category according to standard global BMI classifications.
Using Imperial Units: If the same person weighs 154 pounds (approximately 70 kg) and is 69 inches tall (approximately 1.75 meters):
BMI = 154 / (69 ^ 2) * 703 = 154 / 4761 * 703 = 22.7 (approx.)
In imperial units, the BMI comes out to approximately 22.7, which also falls into the "normal weight" range.
Tip: Slight differences between the two results are due to rounding during conversion. Always use consistent units for accurate results.
BMI FAQs:
If using imperial units: BMI = weight (lb) ÷ [height (in)]² × 703